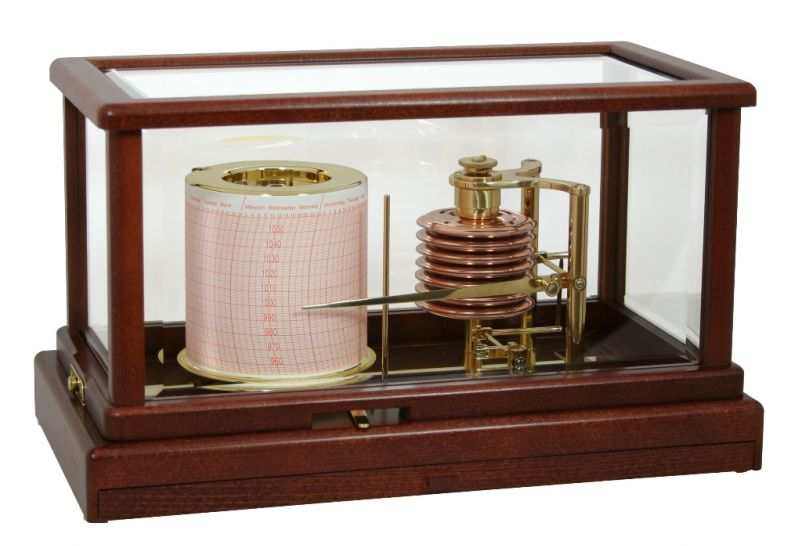
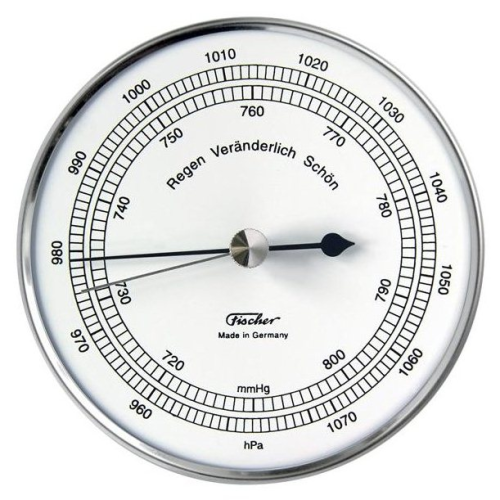
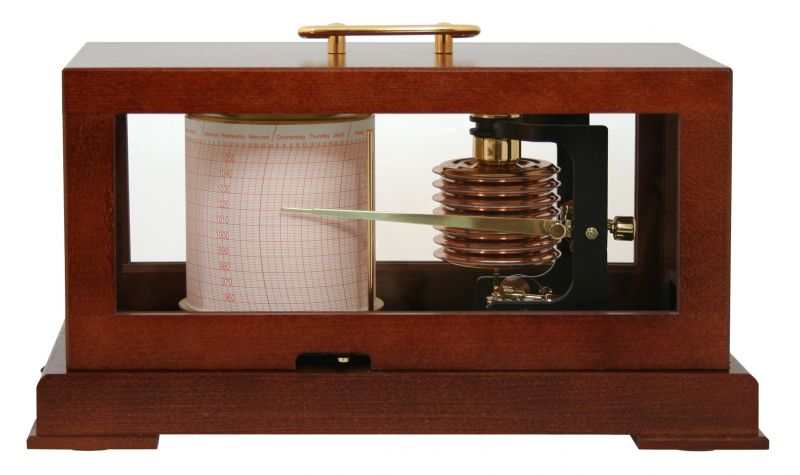
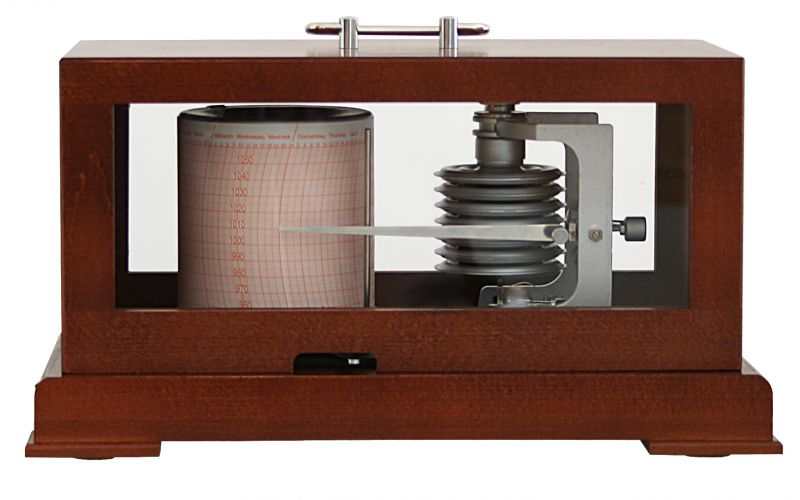
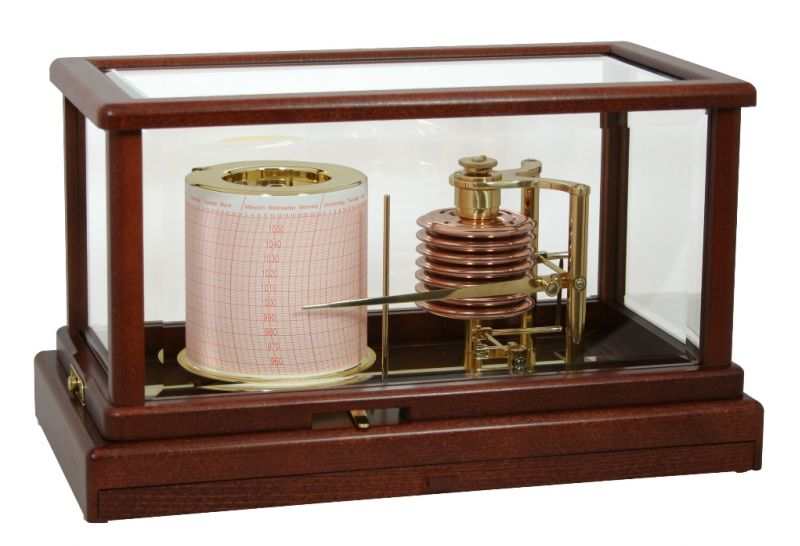
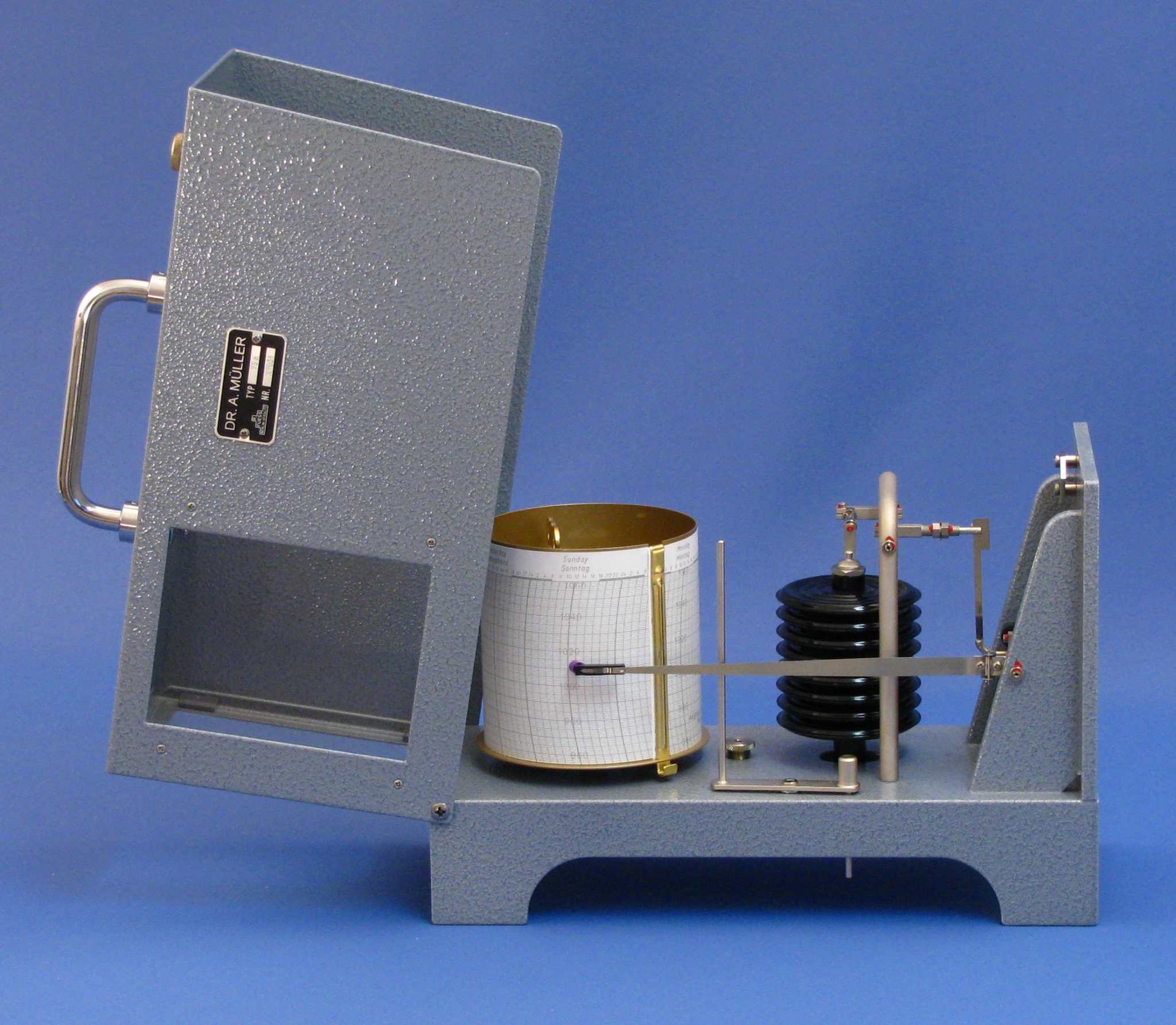
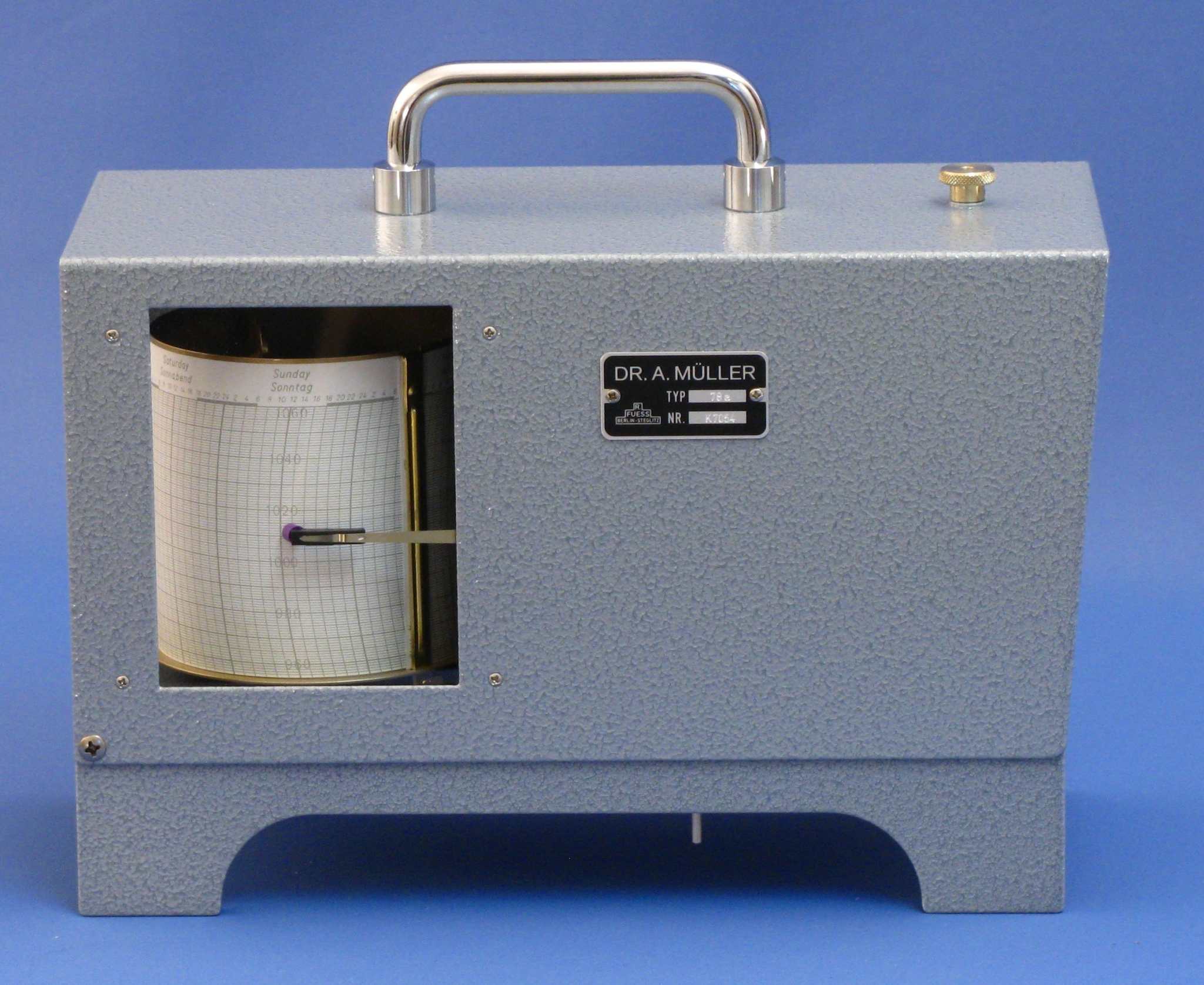
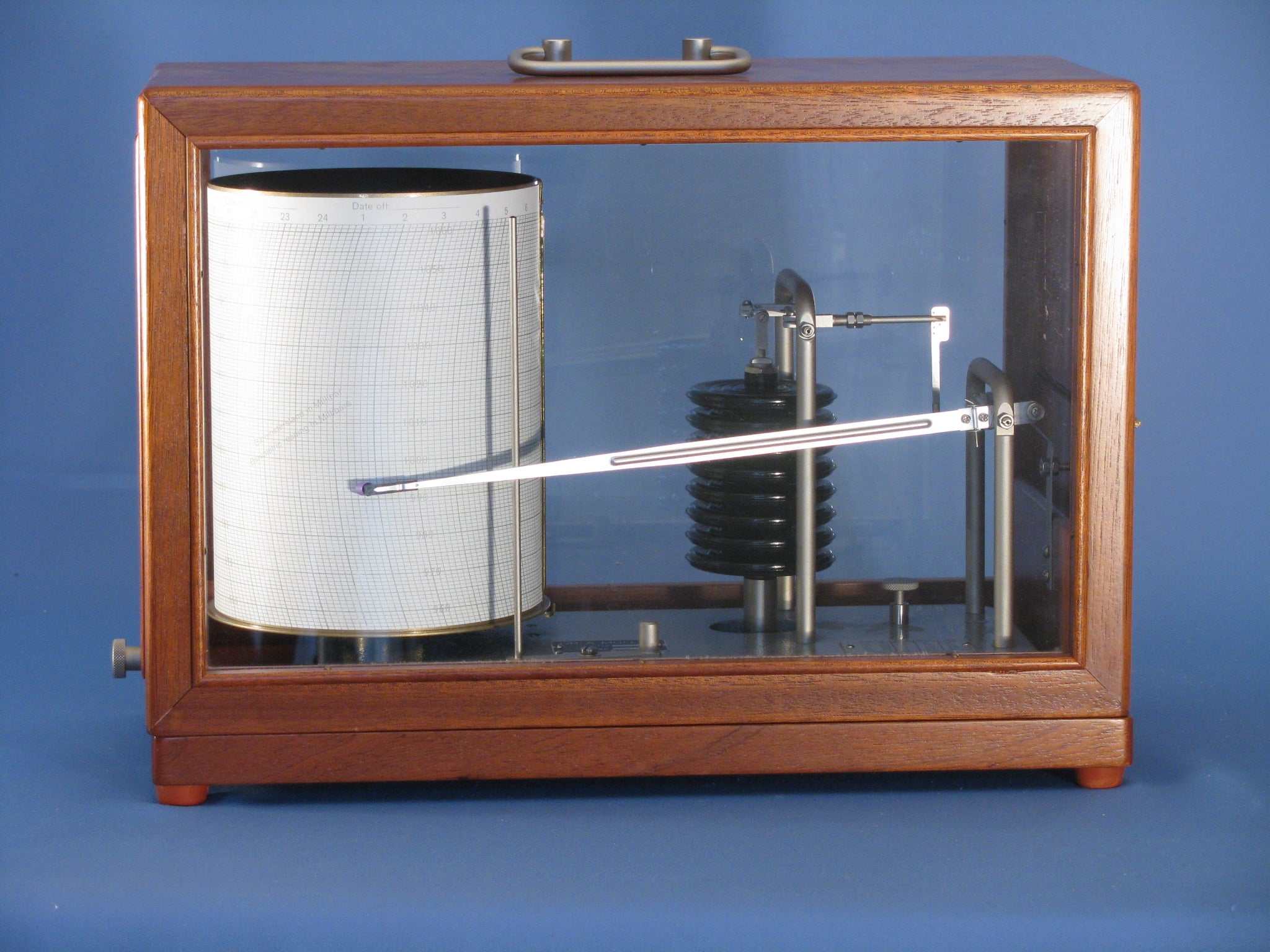
Air pressure measurement
9 products
Showing 1 - 9 of 9 products
Along with temperature, air pressure is one of the oldest quantities measured in meteorology. Pressure is defined as a force relative to a unit of area. The unit of pressure is therefore (unit of force) / (unit of area) , i.e., in the MKS system , N/ m² or Pa (Pascal).
Since this pressure unit is very small, the unit used in meteorology is
hPa (hectoPascal: 1 hPa = 100 Pa ).
This also has historical reasons, as the number given in hPa corresponds to the number given in mbar , which was valid in meteorology for decades.
In addition, there was the unit 1 Torr , derived from the most important atmospheric pressure measuring device, the mercury barometer. 1 Torr is the pressure of a 1 mm high column of mercury, corrected to a mercury temperature of 0 °C and to standard gravity (45° latitude, sea level).
The conversion is therefore carried out according to the relationship:
(1) 1 •10 3 m • 13595 kgm 3 • 9.806 m•s 2 = 1 Torr = 133.32 N • m 2 = 1.3332 hPa
Sometimes, instead of the exact unit Torr , you may also find mm Hg (= mm of mercury). For low pressure (dynamic pressure), you may also find the unit mm WS (= mm water column) = 9.806 Nm"2 -0.1 hPa.
However, the units mbar, Torr, mm Hg and mm WS have not been allowed to be used since 1978.